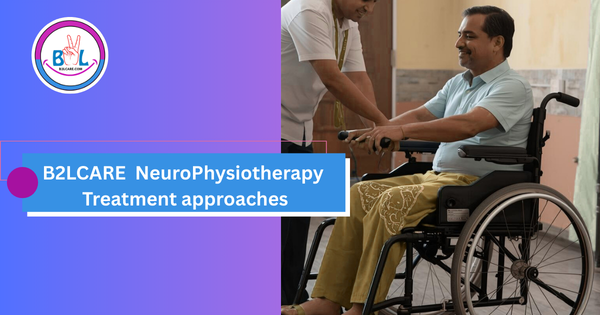
Goal oriented advanced Neuro Physiotherapy Treatment for stroke patient
- Dr Suvradeep Ganguly

- Jun 6, 2025
- 6 min read
Updated: Jun 27, 2025

Advanced neuro physiotherapy for stroke patient
About Brain Stroke?
A brain stroke also known as a brain attack or cerebra vascular accident (CVA), occurs when the blood flow in the brain is disrupted, either by blockage of arteries or due to burst of blood due to rapture of arteries. This interruption deprives brain tissue from oxygen and nutrients leading to cell death and potentially causing lasting damage, disability or even death.
Stroke is classified as two types:
1. Ischemic Stroke: This occurs when blood vessel supplying to the brain is Blocked, often by a blood clot or plaque build-up.

2. Hemorrhagic Stroke: This happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding into and around the brain.
A stroke is a medical emergency. It's crucial to get medical treatment right away. Getting emergency medical help quickly can reduce brain damage and other stroke complications.
Symptoms
If you or someone you're with may be having a stroke, pay attention to the time the symptoms began. Some treatments are most effective when given soon after a stroke begins.
Symptoms of stroke include:
· Trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying. A person having a stroke may be confused, slur words or may not be able to understand speech.
· Numbness, weakness or paralysis in the face, arm or leg. This often affects just one side of the body. The person can try to raise both arms over the head. If one arm begins to fall, it may be a sign of a stroke. Also, one side of the mouth may droop when trying to smile.
· Problems seeing in one or both eyes. The person may suddenly have blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes. Or the person may see double.
· Headache. A sudden, severe headache may be a symptom of a stroke. Vomiting, dizziness and a change in consciousness may occur with the headache.
· Trouble walking. Someone having a stroke may stumble or lose balance or coordination.
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you notice any symptoms of a stroke, even if they seem to come and go or they disappear completely. Think "FAST" and do the following:

· Face. Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
· Arms. Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward? Or is one arm unable to rise?
· Speech. Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is the person's speech slurred or different from usual?
· Time. If you see any of these signs, call 911 or emergency medical help right away.
Primary Impairments after Brain Stroke:
Complications or impairment after stroke depending on the size of the stroke and what part of the brain was affected and also types of stroke ( eg, Hemorrhagic Stroke , Ischemic Stroke, transient ischemic attack Brain steam stroke ).
Sensation:
Sensation is frequently impaired on the hemiplegic side. Impairments are reported in about 53% of stroke patient.
Impairments of sensation includes
1. Superficial sensation
2. Deep sensation
3. Proprioceptive sensation: Proprioception, otherwise known as kinaesthesia, is your body’s ability to sense movement, action, and location without any visual cues . without proprioception, we would not able to move without thinking about next step. Proprioception allows you to walk without consciously thinking about where to place our next feet.
In one study it is shown that about 44% of stroke patient effected by impairment of proprioceptive sensation causing significant difficulties in balance, postural control and motor function impairment.
Pain:
Stroke can result in severe headache or neck and face pain and shoulder pain is most common pain for stroke survivor. Subluxation and rotator cuff weakness is the primary cause of shoulder pain.
Lesion to posterolateral thalamus and spinothalamic system of brain (Back side of our brain) can cause thalamic pain.
Thalamic pain is a constant, burning pain with intermittent sharp pains. Sometimes pains can be triggered by simply stroking the skin, pinprick or contact with heat and cold.
Stroke survivor also suffered from pain due t alter muscle tone ,spasticity or swelling .
Vision Impairments:
Stroke can cause visual field deficits, double vision, or other visual disturbances
Aphasia or other Speech disorders:
Damage to parts of your brain responsible for language may cause aphasia. This condition impairs the expression and understanding of language, as well as reading and writing. Aphasia may occur along with other disorders that impact speech, like apraxia (being unable to perform tasks that were familiar before the stroke) and dysarthria (difficulty speaking).
Weakness:
Weakness or paresis is found in 80 to 90 percent of all patients after stroke and is a major factor in disability. Patients are unable to generate force necessary for initiating and control movement .
This degree of weakness is related to the location and size of the brain injury and varies from a complete inability to achieve any visible contraction of muscle.
Alteration of Muscle:
Flaccidity or Hypotonicity is present immediately after stroke and is due primarily to the effects of cerebral shock. It is generally short-lived lasting a few days or weak. It is generally persisted in small number of patients.
Spasticity (hypertonicity) emerges in the 90% of the patients and occurs on the side of the body opposite of the lesion.
Abnormal Synergy Pattern:
Abnormal and highly stereotyped synergise movement emerges with spasticity. In synergies abnormal movement pattern patient is unable to do and isolated joint movement without producing movement of others joint of same limb.
Her the patient is severely limited in the ability to adapt movements to required task or as per environmental demand.
Altered Motor Programming:
Motor parexis is the ability is planning to execute and coordinated movement. Lesion to the Frontal cortex, left inferior parietal lobe and corpus callosum can produce motor apraxia. In motor apraxia individual struggles to execute learned and purposeful movement despite having normal strength, coordination and sensation.
Postural control and balance:
Balance is disturbed following stroke with impairments in steadiness, symmetry, and dynamic stability common. Problem may exist when reacting to a destabilizing external force (Reactive postural control) or during self-initiated movements. (Anticipatory postural control).
Disruption of central sensorimotor processing lead to an inability to adapt postural movements according to the environmental demand.
Perception and cognition:
Cognitive deficit are presents with lesion involving the cortex and include impairments in alertness, attention, orientation, memory or executive function.
Memory disorder includes impairments in immediate recall, short-term or long-term memory.
Dementia can result from multiple small infracts of the brain, termed multi infract dementia.
Delirium is also known as acute confessional state can result from number of factors following stroke.
Emotional Status:
Lesion of the brain affecting frontal lobe, hypothalamus and limbic system can produce several emotional changes. It is also known as emotional dysregulation. Here 18% of cases is characterised by emotion outburst with crying or agitation.
Depression:
Depression in extremely common, occurring in about one third of stroke cases. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness accompanied feelings of hopelessness, worthless or helplessness. Depressed patient may also experience loss of energy or persistent fatigue, an inability to concentrate.
Goals and Various Advance Neuro Physiotherapy Treatment approaches for Stroke Patient:
Primary goals of neuro physiotherapy treatment for stroke patients are as follows.
1. To improve flexibility and joint integrity
2. To improve strength.
3. Managing spasticity
4. Improve initial movement control
5. Improve motor learning or movement learning.
6. To improve postural control and functional mobility.
7. Improve hand function
8. Improve cognitive function and mental health status.
9. Improve lower extremity function
10. To improve balance and stability
11. Improve gait or walking ability.
12. Improve indoor and outdoor activities.
Recognizing the level of impairment through precise assessment procedures is crucial in ensuring effective treatment. By employing advanced methods such as the Bobath Approach, Neurodevelopmental Techniques, Functional Orientation Approach, Integration Therapy, Biofeedback Therapy, and more, we can significantly enhance the recovery process. Our commitment to these proven strategies will lead to faster and more optimal outcomes for patients, empowering them on their path to rehabilitation.
Still Got questions swirling around in your head? Why not take a moment for yourself and book a free 15-minute tele consultation with our expert physiotherapist! It's the perfect opportunity to get tailored advice and clarity. Don’t wait—let’s tackle those questions together!
To know more about B2LCARE.COM Neuro physiotherapy team visit : https://www.b2lcare.com/neurophysiotherapy
Facebook page : https://www.facebook.com/B2LCARE
You tube channel : http://www.youtube.com/@b2lcarehealthcareathome290

































I read the post about advanced neuro physiotherapy and how it helps stroke patients work on balance, strength, and walking again after serious brain injury, and it made me think of caring for my grandma when she first started her rehab journey at home. At that time I even relied on WGU course help to understand basic patient care terms so I could talk with her therapist more confidently. It reminded me that learning more about care can make you feel calmer and more helpful as a family member.
My health improved 100% when I stopped taking all western medicine and turned to a nutrition lifestyle by changing my eating habits and diet, I avoid prepackaged foods full of chemicals. I purchased Herbal Formula from World Rehabilitate Clinic, I was literally bedbound for about 3 years. But now I have NONE of the issues they diagnosed me with years ago....all done without the help of western medicine. I am not prescribing medicine or supplements but If anyone chose to follow the regimen I chose I will be happy for them, conversely if anyone chooses not to believe, I will fully understand that as I probably wouldn't believe the story if I hadn't lived it.
I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease four years ago. For over two years, I relied on Levodopa and several other medications, but unfortunately, the symptoms kept getting worse. The tremors became more noticeable, and my balance and mobility started to decline quickly. Last year, out of desperation and hope, I decided to try a herbal treatment program from NaturePath Herbal Clinic. Honestly, I was skeptical at first, but within a few months of starting the treatment, I began to notice real changes. My movements became smoother, the tremors subsided, and I felt steadier on my feet. Incredibly, I also regained much of my energy and confidence. It’s been a life-changing experience I feel more like myself again, better than I’ve…
Can Turabian format cover page assignment help improve formatting skills?
Yes, turabian format cover page Assignment Help can definitely improve your formatting skills. The Turabian style has specific rules for cover pages, including title placement, spacing, font size, and other formatting details that students often overlook. With expert guidance, you can learn how to create professionally structured cover pages that meet academic standards. This not only boosts the quality of your assignments but also enhances your understanding of formal formatting styles. For students seeking reliable and expert support, BookMyEssay provides top-notch turabian format cover page Assignment Help, ensuring your work is perfectly formatted, accurate, and ready for top academic performance.